Google Play Flooded With 224 Malicious Apps, 38 Million Downloads Deliver Malware

Massive Scale of the Threat
224 malicious apps identified on Google Play Store collectively amassed 38 million downloads in 2025, according to new research
Click fraud is the most common type of malicious activity, affecting 76% of compromised applications
Businesses running PPC campaigns lose an estimated $3.4 billion annually to invalid clicks generated by these malicious applications
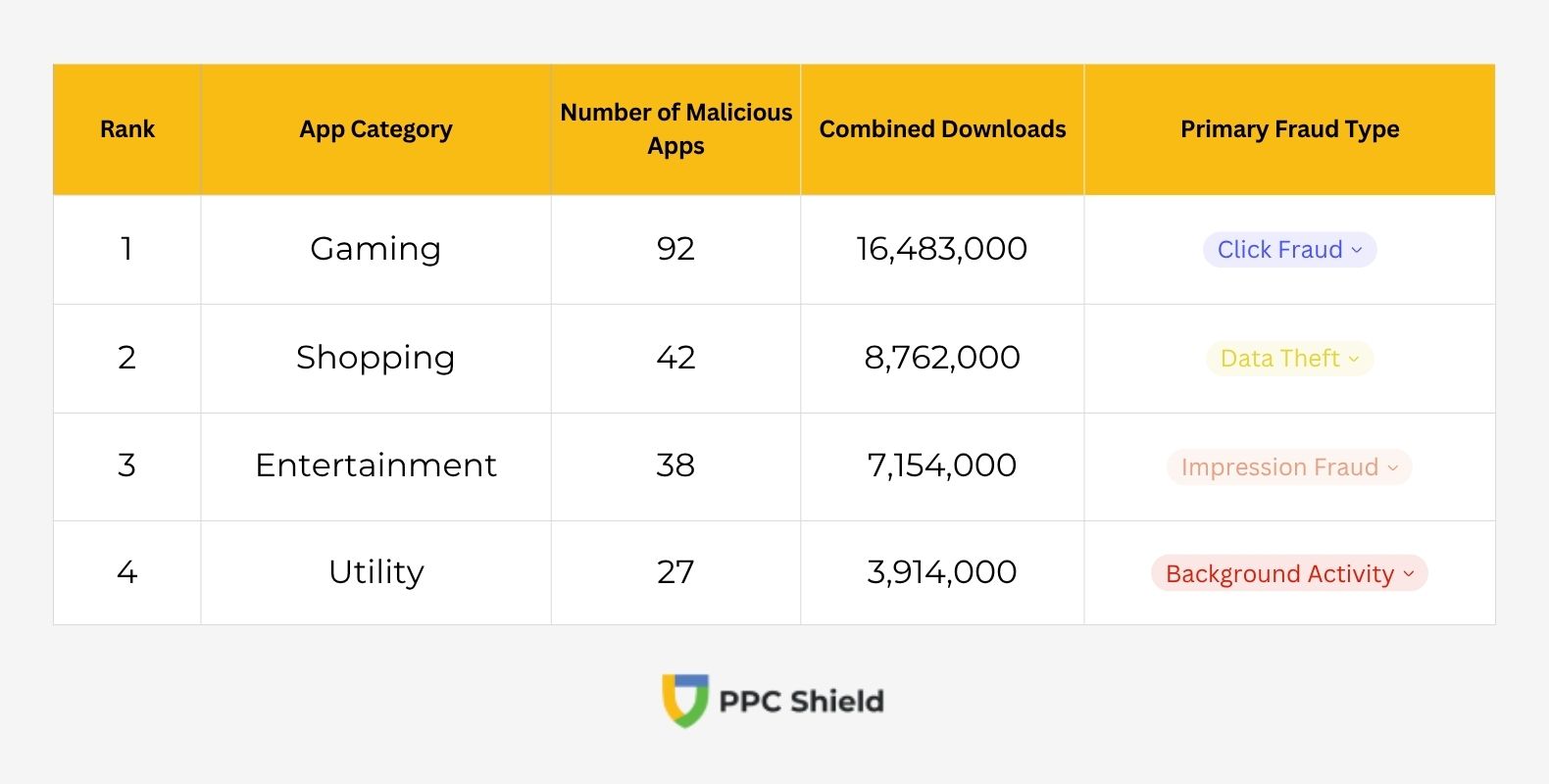
Gaming apps represent the highest risk category with 92 malicious applications identified
A new study has revealed that Google Play Store is hosting 224 malicious applications that have been downloaded 38 million times, with most designed specifically to commit advertising fraud and generate invalid clicks on pay-per-click campaigns.
The study by PPC Shield, a company specialized in detection and prevention of PPC clicks fraud, analyzed applications available on the Google Play Store during the first half of 2025 to identify those containing code designed to generate fake clicks, impressions, and other fraudulent advertising activity.
Click Fraud Dominates Malicious Activity
According to the findings, click fraud is the most damaging type of malicious activity, with 76% of the identified malicious apps engaged in generating fake clicks on digital advertisements. These apps operate in the background, secretly clicking on advertisements while draining device batteries and consuming data.
Shopping category apps rank second among the most dangerous, with 42 malicious applications identified in this category. These applications often request extensive permissions, allowing them to operate without user knowledge and generate revenue for developers through fraudulent ad interactions.
Entertainment apps follow closely behind with 38 infected applications, typically disguised as video players or streaming services. These apps frequently display hidden advertisements that users never see while reporting false impressions to advertising networks.
Utility apps, such as flashlights, calculators, and battery optimizers, contained 27 malicious applications designed to commit ad fraud. These simple apps often have legitimate functionality but run malicious code in the background.
Most dangerous app categories by number of malicious applications
The study also identified the categories with the lowest number of malicious applications, revealing that certain app types present significantly lower risks to users and advertisers.
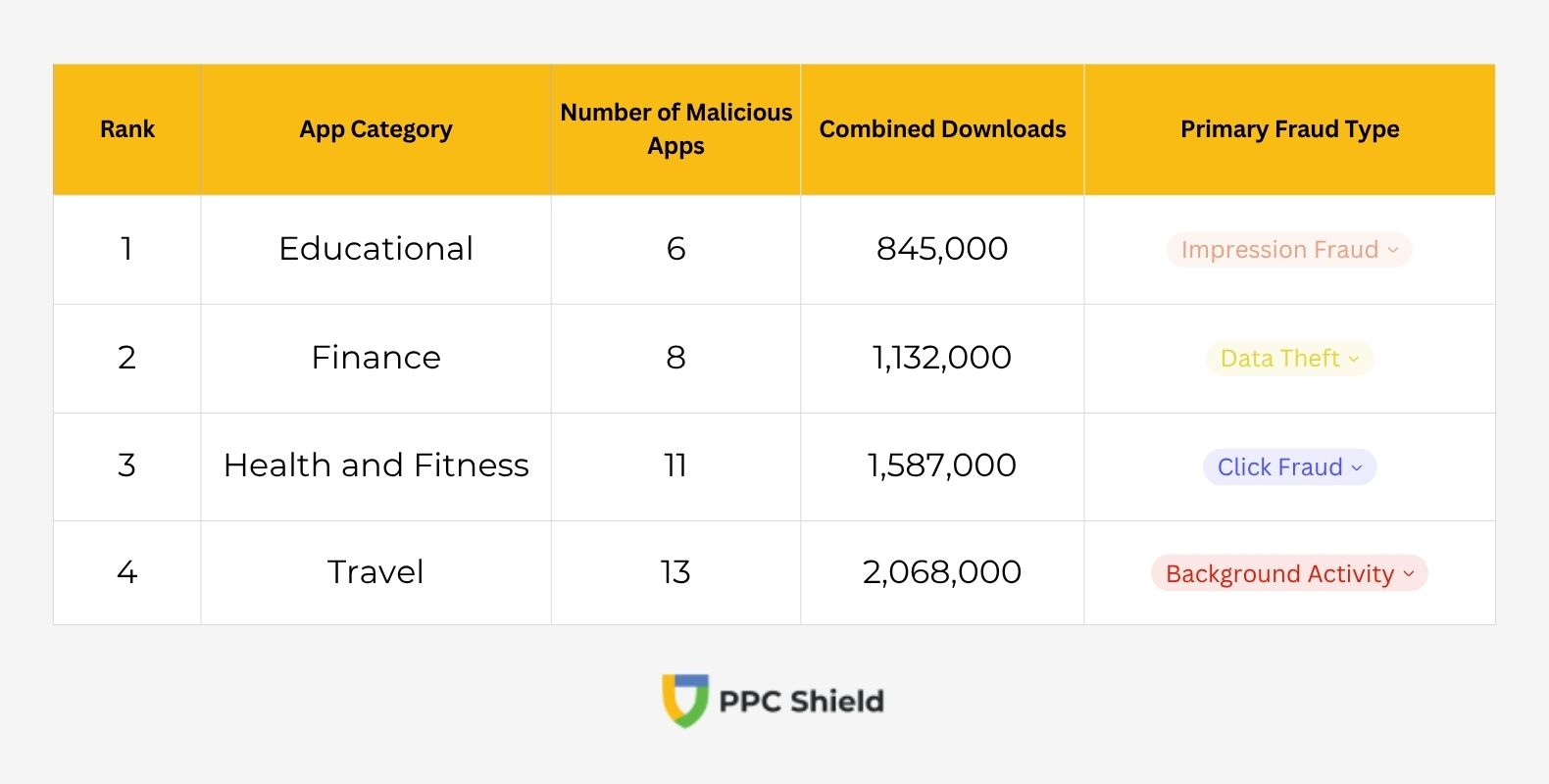
Educational apps showed the lowest infection rate with only 6 malicious apps discovered. These applications typically undergo more scrutiny before being published, as they’re often used by children or in educational settings.
Finance apps contained just 8 malicious applications, likely due to the heightened security standards required for applications handling sensitive financial information.
Health and fitness apps had 11 malicious applications identified during the study period. The relatively low number might be attributed to the specialized nature of these apps and their typically more sophisticated development processes.
Travel apps rounded out the bottom four with 13 malicious applications discovered. These apps tend to have more complex functionality, making malicious code potentially more difficult to hide from Google’s security screening.
Safest app categories by number of malicious applications
Jacques Zarka, spokesperson from PPC Shield, commented on the findings:
“The statistics released today show an alarming trend in how fraudsters are targeting advertising budgets. These 224 malicious apps collectively generated about 38 million downloads, creating a massive network of devices capable of draining advertising budgets through fake clicks and impressions.”
“We found that gaming apps are particularly concerning, as they often request permissions that allow them to run in the background even when not actively used. This creates perfect conditions for click fraud, as these apps can continuously generate fake clicks without the user’s knowledge.”
Zarka added that businesses can protect themselves by implementing specialized monitoring tools:
“As PPC costs continue rising in 2025, businesses need to implement proper protection mechanisms. Unusual patterns in click rates or sudden drops in conversion rates often indicate fraudulent activity. Our analysis shows that companies using click fraud protection typically save between 14% and 26% of their advertising budgets by eliminating invalid clicks.”
The research also found interesting patterns in how these malicious apps operate. Most apps (68%) waited at least 72 hours after installation before beginning fraudulent activities, making detection more difficult for both users and Google’s security systems.
During the first half of 2025, PPC Shield detected that these malicious applications primarily targeted Google Ads campaigns, with 83% of fraudulent clicks occurring on this platform. Facebook Ads were the second most targeted platform at 11%, while other platforms including Microsoft Advertising, Amazon Ads, and TikTok Ads collectively experienced 6% of fraudulent activity.